SAP Business One In-Depth Review: How to Prepare for an MRP Run in SAP B1
In the following article, we continue our exploration of the SAP Business One MRP. Recently, we’ve defined the material requirements planning of SAP B1. Below, we describe how to prepare for the corresponding processes that take place in the ERP system. As you’ve probably guessed already, much of the preparations for an MRP run in SAP Business One take place through the normal routine of using the system. Initially, you need to prepare master data for such areas and entities as items, inventory, purchase orders, production orders, sales orders, bills of material, forecasts, etc. Next, keep all the related information up to date, and MRP will gift you with an accurate view of your requirements.

We can help you integrate SAP Business One with your business. Contact us for further information.
Table of contents
The SAP B1 MRP Process Overview
Note that executing an MRP run in SAP Business One is firstly associated with the accuracy of the provided data. You need to keep control over the information associated with production, supply, and demand.
At the same time, the ERP system offers additional flexibility. Once a run is complete, you can easily address problems that occur during the process. As a result, you maintain smooth production.
SAP Business One MRP Run
The entire MRP run in SAP B1 that covers preparations and further actions looks as follows:
- Manage the MRP-related master data:
- You need to create master data records for both parent and component items utilized in bills of materials;
- Bills of materials for produced goods are required too;
- The same is about bills of materials for items that are utilized in production.
- Manage supply:
- Update purchase and production orders;
- Monitor minimum and maximum inventory levels;
- Run a physical inventory count to see your actual on-hand quantities.
- Manage demand:
- Update sales orders;
- Update sales forecasts.
- Execute an MRP run:
- Choose a short-term period;
- Choose a long-term period.
- Plan production or purchases following the MRP recommendations. You can provide items that are past due or replace them with alternatives. Besides, it is possible to postpone the delivery date, etc.
MRP-Related Master Data Settings
Although the SAP Business One MRP routine may seem a complicated task, at first sight, most of the documents, steps, and data involved are simple and intuitive.
First of all, you deal with production, purchase, and sales orders. These documents list items being bought or sold.
Secondly, the SAP Business One MRP is associated with the three types of master data each of which represents the core of the MRP process:
- An MRP run relies on the bill of materials to figure out what items are used to produce a manufactured item;
- It uses the item data to discover the lead time necessary to acquire each item;
- The MRP tool digs into the inventory data to understand how much of each item is on hand.
Below, we shed light upon how to keep different sorts of master data up to date to make sure that the SAP Business One MRP has an accurate picture of what’s going on within your enterprise and what estimates to generate.
Bill of Materials
So, what’s the purpose of the bill of materials in SAP Business One? This document lists all items used as inputs to a production process. Note that its records can refer to items purchased or made. However, it is required to create separate bills of materials for made items, which may include other made items, etc.
As for an MRP run, it starts with the products in demand, analyzing the relevant bills of materials to see whether required items are available in the necessary quantity.
While some MRP applications have a description of the path items take through labor and production processes, SAP Business One introduces a simplified MRP routine. It does not model production capacity. If you need to include labor costs, use resource master data to represent labor hours or machine capacity.
Item and Inventory Master Data
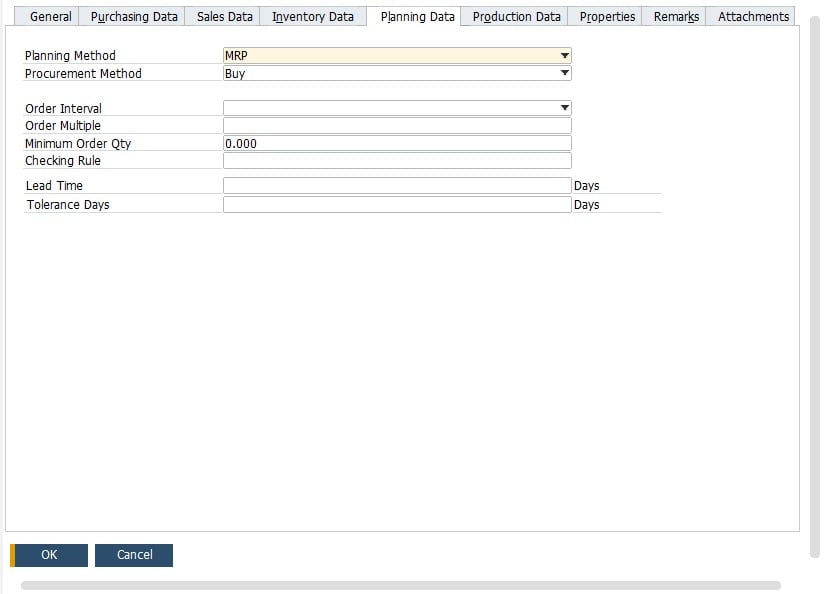
Below, you can see that an Item Master Data window contains the Lead Time field on the Planning Data tab. The SAP Business One MRP heavily relies on it to establish the accuracy and usefulness of the MRP run.
Below, you can see several steps that you need to follow to make sure an MRP run executes correctly:
- Always specify the required and minimum inventory level for each item. You can do that on the Inventory Data tab of the Item Master Data window.
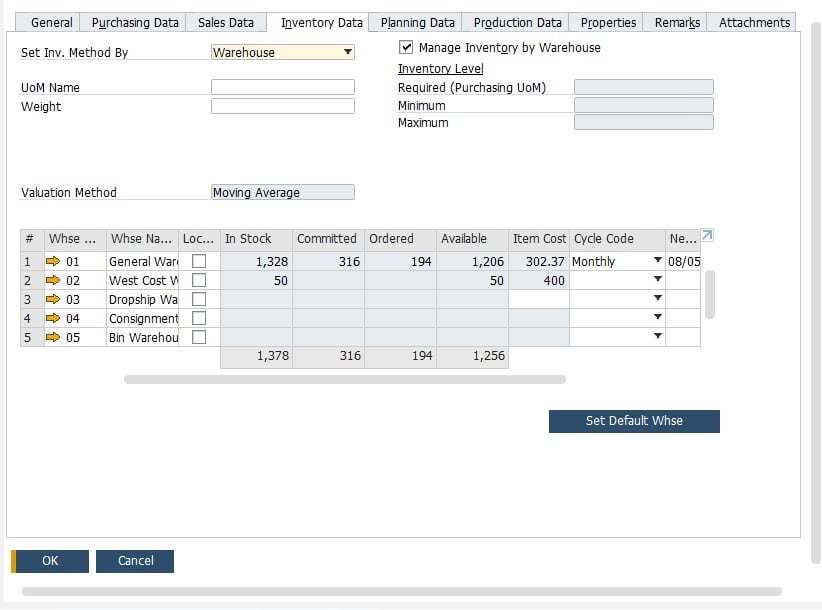
- Switch the planning method per each item to MRP. Otherwise, you won’t be able to select the item in the MRP wizard.
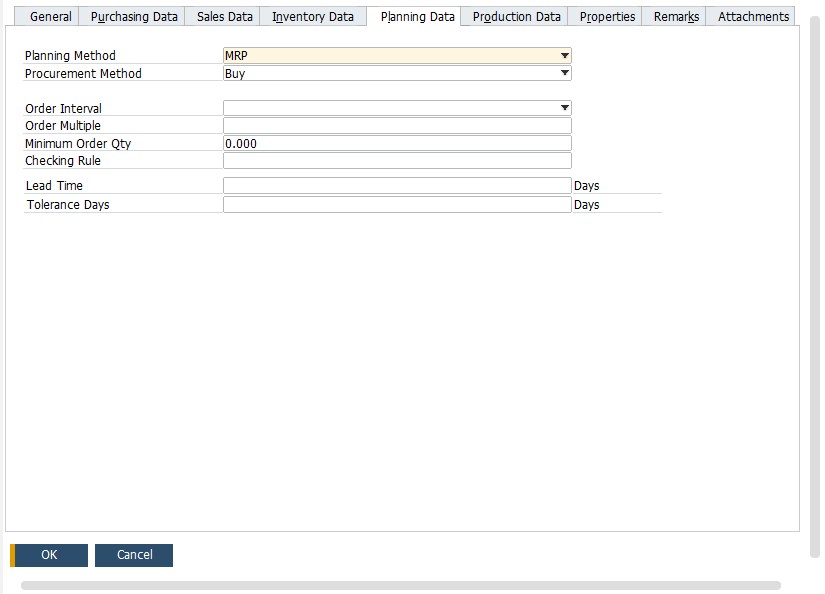
- Define the procurement method per item. It can be “make” (production order is created) or “buy” (purchase document is created). Thus, all items that are parents of a production bill of material must be set to “make”.
- The “make” option also reveals an additional field for a Component Warehouse where you can specify how MRP selects the relevant warehouse.
- Specify item’s order intervals, multiples, and minimum quantity.
- Set checking rules for delivery dates determination in case the Advanced Available to Promise feature is enabled.
- Enter the lead time necessary to purchase or make the item.
- Define the period to tolerate before the demand for the item is satisfied. Specify this parameter outside of the lead time.
- Create sales forecasts if necessary.
How to integrate SAP Business One with external systems
SAP Business One offers numerous tools designed to streamline business processes. Although you can find mechanisms for integration with external systems among them, they are quite limited. But you can extend the default functionality with the help of third-party solutions. For such cases, we provide instruments that enable SAP integrations with core e-commerce platforms. For instance, you can leverage connectors for Magento 2 and Shopify. Don’t hesitate to contact us to get more information on the SAP Business One integration with your business.
Also, check our SAP Business One Integration solution for Magento 2.
SAP Business One Integration FAQ
How to connect SAP Business One to Magento 2
Use the SAP Business One Integration tool to connect Magento 2 to SAP Business One. The connector provides the ability to transfer data between the two platforms via APIs in both directions.
How does the integration work?
The SAP Business One Integration tool creates a direct data flow between your Magento 2 and SAP Business One databases. No third-party servers, platforms, or tools participate in the process.
Is the Magento 2 SAP Business One integration connector an open-code solution?
The tool is open code so that you get full control over it. Feel free to customize the solution according to your needs.
Is it real-time synchronization?
The integrator synchronizes most entities in real-time as you apply the changes.
Can I manage Magento 2 data in the SAP Business One UI?
Yes, you can. With the help of this tool, you can manage products, orders, customers, categories, and other entities right in the user interface of SAP Business One so that all the changes appear in Magento 2.
Which SAP entities can be synchronized with Magento 2?
With the Firebear Magento 2 SAP Business One integration connector, you can leverage the following entities available in the ERP system: Item groups, Items, Price List, Period Discounts, Volume Discounts, Inventory Data, Discount Groups, Discount Groups, Customer Groups, Business Partners, Sales Orders, Deliveries, Business Partners, Business Partner Contacts. At the same time, all the core Magento 2 entities can be provided to SAP Business One.

