Magento 2 Components (module, theme, language packages)

Below, you will find a post about the definition, installation, and structure of Magento 2 components. If you are new to the platform, the following information will help you get a deeper insight into Magento 2. If you do not understand the difference between modules and components or have no ideas about the Magento 2 component structure, then you’ve come to the right place.
How to install Magento 2 modules

While most newbies think that there is no difference between a module and a component and both are just synonyms, they are mistaken, because a module is just one of component types. Other components are gathered under themes and language packages.
While a module is entirely based on code that extends the behavior of the platform, a theme changes its look and feel and a language package is used for translating text in your Magento 2 app. All these components are available on Magento Connect.
Table of contents
Magento 2 Component File Structure
The following section describes the component structure of Magento 2. This aspect is vital, since Magento 2 relies on particular places inside the module file structure. Consequently, it is necessary to follow the predefined file structure, otherwise your module will never work as expected.
Root Directory
A component’s root directory is the top-level directory, which contains the code of the component. The recommended subdirectory for app to be used:
- app/code – for modules
- app/design/frontend – for storefront theme
- app/design/adminhtml – for Magento Admin theme
- app/i18n – for language packages
To set up this environment, clone the Magento 2 GitHub repository.
Please note that you get the vendor directory structure after using the composer create-project command or a compressed Magento 2 archive.
Required files
All components require using the following files:
- registration.php
- composer.json
Magento 2 Component File Structure: Module File Structure
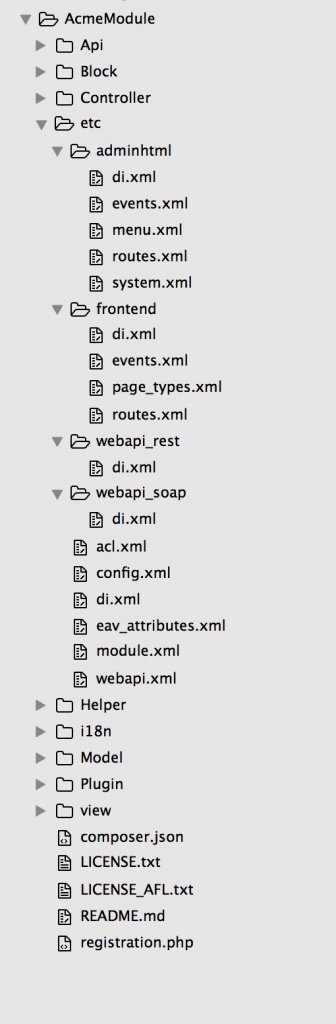
A typical Magento 2 module has the following file structure:
In their turn, the structure includes the following typical module directories:
- Block: PHP view classes (module logic and its MVC vertical implementation)
- Controller: PHP controller classes (module logic and its MVC vertical implementation)
- etc: configuration files (such as module.xml)
- Model: PHP model classes (module logic and its MVC vertical implementation)
- Setup: module database structure classes + data setup classes (utilized for installations or upgrades)
As for additional directories, they are:
- Api: PHP classes exposed to the API
- i18n: localization files
- Plugin: plug-ins
- view: view files (static view and layout files, design and email templates)
Additional directories are used to configure ancillary functions. They are utilized in case of internationalization, plug-ins, and layout files.
Magento 2 Component File Structure: Theme File Structure
A typical theme file structure in Magento 2 looks as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
├── composer.json ├── etc │ └── view.xml ├── i18n │ └── en_US.csv ├── LICENSE_AFL.txt ├── LICENSE.txt ├── media │ └── preview.jpg ├── registration.php └── web ├── css │ ├── email.less │ ├── print.less │ ├── source │ │ ├── _actions-toolbar.less │ │ ├── _breadcrumbs.less │ │ ├── _buttons.less │ │ ├── components │ │ │ └── _modals_extend.less │ │ ├── _icons.less │ │ ├── _layout.less │ │ ├── _theme.less │ │ ├── _tooltips.less │ │ ├── _typography.less │ │ └── _variables.less │ ├── _styles.less │ ├── styles-l.less │ └── styles-m.less ├── images │ └── logo.svg └── js ├── navigation-menu.js ├── responsive.js └── theme.js |
This file structure contains the following directories:
- etc: view.xml with image configurations
- i18n: translation dictionaries
- media: a preview of a theme
- web: static files
The web directory is optional. It contains the following subdirectories:
- css/source with less configuration files and the theme.less file
- css/source/lib with View files for overriding the UI library files
- fonts with fonts
- images with static images
- js with JavaScript files
Magento 2 Component File Structure: Language Package Structure
A typical language package structure in Magento 2 looks as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
├── de_de │ ├── composer.json │ ├── language.xml │ ├── LICENSE_AFL.txt │ ├── LICENSE.txt │ └── registration.php ├── en_us │ ├── composer.json │ ├── language.xml │ ├── LICENSE_AFL.txt │ ├── LICENSE.txt │ └── registration.php ├── pt_br │ ├── composer.json │ ├── language.xml │ ├── LICENSE_AFL.txt │ ├── LICENSE.txt │ └── registration.php |
Please note that the top-level directory is the only required directory here. Another strict requirement is the necessity to use lowercase for the directory name. It is also recommended to name the directory according to the code.
Magento 2 Component Registration
As you might have guessed, Magento 2 components must be registered in the system. Use the Magento ComponentRegistrar class to achieve this goal. Add a registration.php file to each component’s root directory.
Magento 2 Component Registration: Modules
Register modules within the Magento 2 system as follows:
|
1 |
ComponentRegistrar::register(ComponentRegistrar::MODULE, '<VendorName_ModuleName>', __DIR__); |
- <VendorName> illustrates the name of the company that provides the module
- <ModuleName> shows the module’s name.
The official documentation provides the following example of the module registration in Magento 2:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
\Magento\Framework\Component\ComponentRegistrar::register( \Magento\Framework\Component\ComponentRegistrar::MODULE, 'Magento_AdminNotification', __DIR__ ); |
Magento 2 Component Registration: Themes
Register themes within the Magento 2 system as follows:
|
1 |
ComponentRegistrar::register(ComponentRegistrar::THEME, '<area>/<vendor>/<theme name>', __DIR__); |
- <area> illustrates the module’s functional area, such as frontend or controller
- <vendor> shows the company’s name related to the theme provider
- <theme name> indicates the theme’s name
The official documentation provides the following example of the theme registration in Magento 2:
|
1 |
ComponentRegistrar::register(ComponentRegistrar::THEME, 'frontend/Magento/luma', __DIR__); |
Magento 2 Component Registration: Language Packages
Register language packages within the Magento 2 system as follows::
|
1 |
ComponentRegistrar::register(ComponentRegistrar::LANGUAGE, '<VendorName>_<packageName>', __DIR__); |
- <VendorName> illustrates the name of the company that provides the package
- <packageName> shows the package’s name
The official documentation provides the following example of the language package registration in Magento 2:
|
1 |
ComponentRegistrar::register(ComponentRegistrar::LANGUAGE, 'magento_de_de', __DIR__); |
Magento 2 Component Registration: registration.php and composer.json
When you have a registration.php file, it is necessary to create an appropriate composer.json file and invoke your registration.php in it. Use the composer.json autoload section:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
{ "name": "Acme-vendor/bar-component", "autoload": { "psr-4": { "AcmeVendor\\BarComponent\\": "" }, "files": [ "registration.php" ] } } |
The official documentation provides the following sample registration.php file:
|
1 2 3 |
<?php use \Magento\Framework\Component\ComponentRegistrar; ComponentRegistrar::register(ComponentRegistrar::MODULE, 'Magento_AdminNotification', __DIR__); |
Magento 2 Component Load Order
Use your component’s composer.json to specify your component’s dependency. Component can be dependent on other components or files from other components. It is also important to specify a load order. Do it in the component’s module.xml file with the aid of the <sequence> tag. Thus, you will ensure that all necessary files from other components are loaded on time.
If you are not familiar with the <sequence> tag, it is used for declaring components that must be loaded previously to your current component. You can use it with configuration files, setup classes, view files, etc.
It is also necessary to mention that <sequence> provides zero influence on the loading of regular or non-setup classes. As for Setup classes, they update or create database schema or data.
If a component’s logic is dependent on something from another component, add it to:
- require in composer.json
- <sequence> in module.xml
Please note that the load order does not take any effect, if you’ve changed the component load order via the <sequence> tag, but did not regenerate the component list in the config.php file. Enable the component using the following command, to achieve this goal:
|
1 |
magento component:enable <component-list> |
- <component-list> – components with the <sequence> tag.
Avoid creating circular dependencies when using <sequence> in multiple components, otherwise Magento 2 will abort the installation.
Magento 2 Components: How To Create A Component
Creating a component requires to major steps to be performed:
- Adding the module.xml file
- Adding the composer.json file
Both procedures are described below.
module.xml
First of all, you should add a module.xml file to the /etc folder to declare the component itself.
The official documentation provides the following example of the smallest working module.xml:
|
1 2 3 |
<config> <module name="Vendor_ComponentName" setup_version="2.0.0"/> </config> |
- name – your component’s name
- setup_version – the Magento version used by your component
Both attributes are necessary.
composer.json
The official documentation provides the following example of the composer.json file:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
{ "name": "your-name/module-Acme", "description": "Test component for Magento 2", "require": { "php": "~5.5.0|~5.6.0", "magento/module-store": "1.0.0-beta", "magento/module-catalog": "1.0.0-beta", "magento/module-catalog-inventory": "1.0.0-beta", "magento/module-ui": "self.version", "magento/magento-composer-installer": "*" }, "suggest": { "magento/module-webapi": "1.0.0-beta" }, "type": "magento2-module", "version": "1.0.0-beta", "license": [ "OSL-3.0", "AFL-3.0" ], "autoload": { "files": [ "registration.php" ], "psr-4": { "Magento\\CatalogImportExport\\": "" } } } |
- name – your component’s name
- description – your component’s purpose explanation
- require – your component’s dependencies
- suggest – soft dependencies (component load order is not affected)
- type – component type (magento2-theme, magento2-module, magento2-language)
- version – your component’s version.
- license – applicable licenses
- autoload – composer’s instructions related to loading specified files.
Magento 2 Components: How To Package A File
It is relatively easy to package a component in Magento 2. You only have to:
- Create a composer.json file (it is also called a Magento Composer file)
- Register the component via the registration.php file
- Package your Magento 2 component
- Publish the component
For further information on these steps, check the following link: .
Magento 2 Components: How To Resolve Component Dependency Conflicts
All common component dependency conflicts in Magento 2 are divided into three groups: Conflicting dependencies; File system permissions issues, and problems related to the Component Dependency Check status (it never changes).
Let’s describe conflicting dependencies first. If you see the following message:
|
1 |
We found conflicting component dependencies |
It means that Composer is not able to determine which components to update or install. Component dependency issues in Magento 2 can be resolved only if you are a technical specialist who knows how Composer works. The procedure requires editing the composer.json file.
As for file system permissions issues, they cause the following message:
|
1 2 |
file_put_contents(/var/www/html/magento2ce/var/composer_home/cache/repo/https--- packagist.org/provider-doctrine$instantiator.json): failed to open stream: Permission denied |
In order to solve any system permissions issue, you should set file system permissions properly.
If the Component Dependency Check status doesn’t change, delete or rename the following files:
|
1 2 3 |
<your Magento install dir>/var/.update_cronjob_status and <your Magento install dir>/var/.setup_cronjob_status |
and rerun the Component Manager.
Sources