DIY SEO: Google PageRank

It is hard to imagine how much e-commerce depends on search engine rankings nowadays. Numerous websites continuously compete against each other for the right to get to the top positions in Google search results with the ultimate aim of driving more traffic and attracting more potential customers. It is widely known that the most proven way to get good rankings is through creating high-end content which is likely to be relevant to other websites and users. Being relevant to people equals being relevant to search engines – this is the concept underlying Google’s famous link analysis algorithm that has been successfully used for years to rank websites effectively based on their potential importance to internet users. So, this is our extensive guide on everything that concerns Google PageRank, its main features, SEO implementation methods, and many more. And as you might have guessed, the guide is fully compatible with Magento!

Table of contents
What is Google PageRank?
Plainly speaking, Google PageRank is an automated algorithm that constantly measures, evaluates, and eventually ranks all existing web pages on the Internet in accordance with their relevance to the user. The relevance is built upon the assumption that the more incoming links a website has, the more important it is. In other words, a website is likely to get higher rankings by being “cited” by as many websites as possible. Moreover, the relevance will also depend on how relevant the citing websites themselves are. What Google PageRank does not consider, however, is the actual content quality of the page.
The idea behind seeking high rankings is that most web surfers tend to only pay attention to the first few search results, which is why these primary positions are important for attracting more traffic to a website and thus important for search engine optimization.
Google PageRank appeared to be the first algorithm written for a new type of search engine by Larry Page and Sergey Brin at Stanford in 1996, two years before they founded their worldwide famous company. The name of the algorithm has a well-formed pun accumulating both the concept of a web page and one of its developers’ names.
There are other secondary tools embedded in the Google Search engine that make the whole PageRank’s job even more accurate, but we should not underestimate the possibilities this ranking algorithm alone is capable of. Apart from being the first algorithm introduced by the company, it also happened to become the fundamental part of other Google-based search tools as well as the most discussed Google feature among the internet community.
How does PageRank actually work?
Google PageRank’s algorithm performs relevance measuring of each element included in hyperlinked data set through the process of numerical weighting which allows for defining the relative “importance” of particular internet pages. Numerical weighting is performed in such a way that some elements will eventually be given more priority as opposed to others. As a result, some pages on the same website can be ranked higher than others. The resulting weight of the given page (or element E) will then be presented as the PageRank of E or PR (E).
PageRank’s mathematical algorithm is originally based on web graph principles, presenting all webpages as nodes and directed links as their edges. Authority pages, such as those having top-level domains, are considered to get higher rank values from the algorithm than hub pages, and higher overall relevance, accordingly. Additional hyperlinks to a page will be regarded as bonus votes during PageRank’s analysis. Thus, a page having the most of incoming links from as many highly ranked pages as possible will itself get a high rank.
This algorithm is often exposed to criticism, as it accepts the possibility of granting a high rank to a web page that has no actual relevance or authority in terms of its content. That is why numerous studies are still being conducted in order to find a way to ignore incoming links to pages having falsely influenced PageRanks.
PageRank calculation
At its core, Google PageRank assigns a probability to each analyzed element in the data set that a user is likely to click on a link that will eventually lead him to a given web page. Such probability distribution is said to be evenly divided among all web documents at the starting point of the algorithm’s analysis. Furthermore, PageRank goes through a set of periodic passes (or iterations) in order to assign the exact value to each element of the set thus approaching the real page value. So, if a page has a PageRank of 0.5, that means that it has a 50% chance that a user will randomly get to it by clicking on a random link.
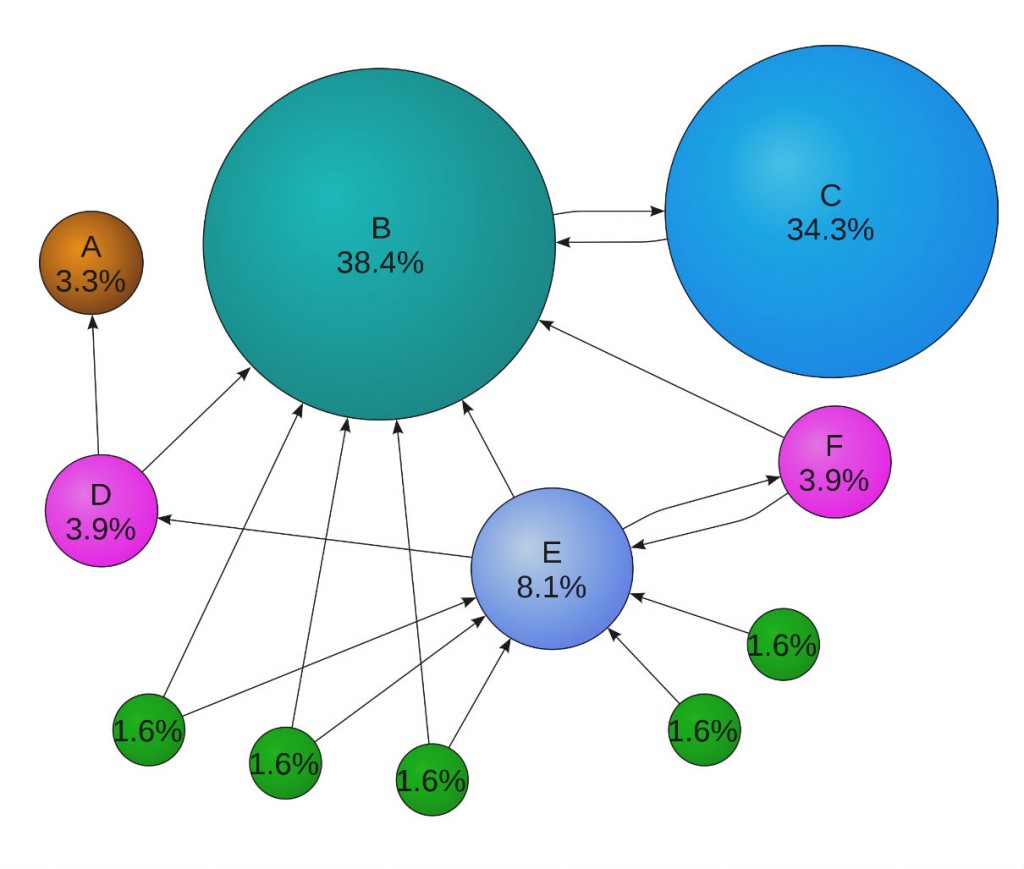
As a basic example, we will take pages A, B, C, and D as the elements included in PageRank’s data set. According to the original PageRank theory, the total PageRank value for all web pages can get the maximum value of 1 (more precisely – any value from 0 to 1). If to assume that the total value of pages A, B, C, and D equals 1, then the PageRank of each separate page will be 0.25. Now, we should connect these pages by distributing corresponding backlinks among them. Let’s say, page B has outbound links to pages C and A, page D has outbound links to pages B, C, and A, and page C has an outbound link to page A. As a result, all pages give equal shares of their value to other page or pages except for A which has no backlinks at all. Because page A does not lose its original value of 0.25 but also receives more shares from all its neighboring pages, it eventually increases its total value to 0.458 thus getting higher general relevance.
Mathematically speaking, this whole calculation process can be presented in the following equation:
PR(A) = (1-d) + d(PR(T1)/C(T1) + … + PR(Tn)/C(Tn)), where
- d is a damping factor representing the probability that, at any step, a user will continue clicking on random links. Although this probability can be anything from 0 to 1, it is generally assumed that a damping factor has an approximate value of 0.85. It is done to minimize the excessive external influence on a given page;
- (1-d) is, accordingly, a “normalized” or average sum of all pages in the data set. This element also guarantees that, if a page does not have any backlinks at all, it will still possess a minimal PageRank value (1-0.85);
- T1…Tn are pages containing URLs pointing to page A;
- PR(T1)/C(T1)+…+PR(Tn)/C(Tn) – the total share of a value transferred to page A from pages T1 to Tn;
- d(…) is the total value amount received by page A through all existing backlinks and normalized by damping factor d.
The number of iterations for each PageRank analysis will depend on the total number of analyzed web pages. In the original study of Page and Brin, PageRank algorithm analyzed the network of 322 million web pages by going through 52 iterations. In fact, the more iterations there are, the more accurate the final result is going to be.
Where else is Google PageRank used?
While being a fundamental part of Google’s search engine, Google PageRank is integrated into numerous accessory processes and web tools developed by the company’s developers in order to boost the search engine’s overall efficiency. Here are some of them.
SERP
The SERP, or the search engine results page, is a web page containing a search engine’s reply to an actual query based on its keywords. It usually contains a list of the most relevant links pointing to associated web pages accompanied by content-related bits of text below. The position of a link will depend on its PageRank, so the higher rank a web page has, the higher position in the SERP it will get. However, there are many other factors contributing to the final placement of a page in the search results list. For instance, PageRank itself does not take into account page keywords for defining its relevance. The SERP’s algorithm, however, provides relevance which can be directly referred to the user as he sets an initial request to the search engine by entering a specific sequence of keywords. So when PageRank determines a set of the most relevant or authoritative pages, the eventual sequence of those pages in the SERP will depend on whether they contain the required keywords and, if yes, how well they respond to the user’s query in terms of general content.
The SERP’s sensitivity to keywords has a large potential in the field of SEO, which means that website owners can improve their positions in the search results list by analyzing the most popular keywords and keyword sequences and integrating them into the content of particular web pages.
Google Toolbar
Google Toolbar is a specialized toolbar for Internet Explorer that can also display a PageRank of a viewed page. It usually shows an approximate value between 0 and 10 to provide the relevance of a given web page. However, it is not known whether Google PageRank’s official algorithm is used to determine this value. Moreover, while PageRank is set to update page value regularly, the data provided by Google Toolbar are often outdated.
nofollow links
Since 2005, Google has introduced the nofollow value that can be assigned to rel attribute of a HTML link telling search engines not to consider the weight of a specific URL when calculating the value of a target page. It was originally done to prevent users from backlink spamming in other websites’ blogs and comments in order to boost PageRanks of their own pages. However, many web developers made use of this feature. By blocking PageRank weight for some of their internal links, they eventually expected their other pages to get more weight. Google managed to figure out this trick and later modified the nofollow system in such a way that PageRank would define the value of a page considering both follow and nofollow outgoing links while passing the actual weight only through normal or follow URLs.

It is nevertheless tempting to find alternative ways of avoiding nofollow limitations for SEO purposes. For now, several techniques have been introduced; JavaScript implementation and iframe tagging are among them.
Manipulations with Google PageRank
With the gradual growth of the e-commerce niche, PageRank became the basis for a new type of business that allowed website owners to boost their ranks in the fastest way possible. Since then, numerous companies have been founded that specialize in selling highly ranked links for SEO, and the price for them varies depending on their overall value. Buying backlinks is still widely considered one of the most efficient moves in a SEO marketing strategy, as it helps to sufficiently increase popularity and attract more traffic to a particular website. However, Google keeps watch over this kind of activity and strongly punishes those involved in backlink trade by devaluating the URLs concerned.
External PageRank use
Google PageRank became of use to many other internet projects and services due to its general applicability. Its principles are used for social metrics and other types of data analysis, bibliometrics, and even in sciences, including physics, biology, and chemistry. Particularly, we can meet PageRank in:
- Twitter’s recommendations that are formed based on its own personalized PageRank;
- Swiftype whose SEO services include providing websites and mobile apps with individual PageRanks and enterprise search solutions;
- Academic journals’ relevance value, proposed as an alternative to the impact factor which was earlier introduced by Institute for Scientific Information;
- Web crawler’s own algorithm as a primary metric based on which it will or will not index a particular web page;
- Scientific methods, such as those that could help to measure the impact of a particular community on the whole network.
- and any other virtual or real network-based systems for analyzing and measuring their performance.
Disadvantages of Google PageRank
Despite the huge importance Google PageRank has in terms of defining relevant web pages on the Internet, there are several drawbacks that make it less appealing to the user:
- It is a completely automated algorithm that does not involve the presence of real people, which is often a disadvantage, as there are many ways to cheat on the system.
- PageRank often takes into account such factors as age, which means that older pages automatically have more chances to get higher page ranks.
- Artificial inflation of a PageRank won’t work if you simply create dozens of empty links pointing to your website’s page. Moreover, it can be even more dangerous, for Google can take appropriate measures and devaluate an entire website’s rankings.
- Although Wikipedia is considered an authoritative source, using links from it is unlikely to influence your PageRanks. However, it is possible that using Wikipedia-based content will do.
Google PageRank tools
You can effectively monitor and improve your own website’s relevance by using one of the following PageRank tools and services, which are also suitable for the Magento platform.
- . This tool can be used both to check the website’s PageRank and to check the PageRank of a specific web page.
- . This calculator will provide you with the most accurate results that are likely to diverge from the ones shown in Google Toolbar but will approach to original PageRank numbers.
- . This tool is a visual guide that helps see which incoming links give more value to a given page. It also shows links with nofollow status.
- /. With the help of these free tools, you can get PageRank information from several data centers and get regularly informed about the latest updates of your PageRank via e-mail.
- . The tool will provide you with PageRank results based on more than 700 Google data centers.
- This service specializes in checking websites’ popularity and trying to predict the estimated PageRank of a given page in the future. The results should not be considered accurate, though.
- . The creators of this tool highly recommend using it for monitoring the page ranks of your competitor’s websites, but you can also check the relevance of your own. The tool can analyze and sum up individual values of each website page to give you the overall website PageRank, which is quite useful in the case of Magento websites with lots of pages.
- . This is a demo version of a multi-task service that can not only check your PageRank but also help you effectively organize your web pages. Particularly, you can create a visual graph and connect them among each other with corresponding links.
- . A comprehensive list of positive as well as negative Google ranking factors will help you to better understand how PageRank actually works and how to adjust your Magento website and SEO marketing campaign for giving a natural boost to your website ranking.









