Micro & Macro Environment Factors & Their Role in E-Commerce Success

The dynamic world of e-commerce constantly shapes businesses that face both internal and external forces or micro and macro environments. Understanding the difference between micro environment or internal factors and macro environment or external factors is crucial for navigating this landscape effectively. While micro factors — such as customers, suppliers, and competitors — can be directly influenced and adjusted by the business, macro factors — like economic trends, regulations, and technology — exist beyond a company’s control, shaping the broader context in which it operates.
Micro environment factors impact daily operations, allowing businesses to react swiftly to shifts in customer preferences or supplier issues. In contrast, macro environment factors affecting business require strategic foresight, as they dictate long-term planning and adaptation. A sudden regulatory change or economic downturn can force businesses to pivot quickly, testing their resilience.
In this guide, we’ll explore what micro and macro environment factors are, highlight their differences, and show their real-world impact on e-commerce. You’ll find SWOT analyses, practical strategies for leveraging these factors, and tips on mitigating risks. By understanding both the internal and external influences, you can better position your e-commerce business for success — turning potential threats into opportunities for growth.

Table of contents
- 1 What Are Micro Environment Factors?
- 2 What Are Macro Environment Factors?
- 3 Key Differences Between Internal and External Factors
- 4 SWOT Analysis for Micro and Macro Environment Factors
- 5 Mitigating the Impact of Micro and Macro Environment Factors in E-Commerce
- 6 Conclusion: Navigating the Complex Landscape of Internal and External Factors
What Are Micro Environment Factors?
In e-commerce, micro environment factors are the immediate elements that directly impact daily business operations. Unlike macro environment factors, which involve broader economic and societal trends, micro environment factors are those that a company can directly influence or interact with frequently. These include key players like customers, suppliers, and competitors — elements that are crucial in shaping your e-commerce strategy and performance.
List of Key internal Factors Affecting E-Commerce
- Customers: The Driving Force Behind Your Business. Customers are at the heart of every e-commerce operation. Their preferences, behaviors, and buying trends directly influence what products you offer and how you market them. Understanding customer needs isn’t just important — it’s the foundation of any successful e-commerce strategy.
- Suppliers: Your Backbone in the Supply Chain. Suppliers are a vital part of the micro environment that provides the products or raw materials you sell. Reliable suppliers ensure smooth operations, while disruptions can lead to stockouts and lost sales.
- Competitors: The Ever-Present Challenge. Competitors shape your market landscape by influencing pricing strategies, product offerings, and marketing tactics. E-commerce is fiercely competitive, and staying ahead requires constant monitoring of what others are doing.
- Intermediaries: The Unsung Heroes of E-Commerce. Intermediaries, such as logistics partners, payment gateways, and affiliate networks, play a crucial role in facilitating your operations. They are the bridge between your business and customers, ensuring orders are fulfilled and payments are processed seamlessly.
- Public Relations and Media: The Voice of Your Brand. Public perception and media coverage can significantly impact your brand’s reputation. A positive review in a major publication can drive traffic and sales, while negative press or social media backlash can lead to boycotts and reduced customer loyalty.
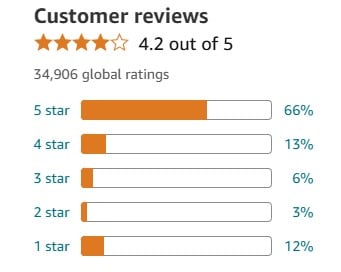
Customer ratings and reviews illustrate customer preferences which is a micro environment factor
Impact of Micro Environment on E-commerce
Understanding and effectively managing internal factors can make or break an e-commerce business. For instance:
- Customers: A deep understanding of customer preferences can boost sales and foster loyalty, as seen when companies like Amazon use data-driven insights to recommend products tailored to individual shoppers.
- Suppliers: Maintaining strong relationships with multiple suppliers can prevent disruptions, ensuring a steady flow of products even when one partner experiences issues.
- Competitors: Monitoring competitor activities allows you to quickly adapt your strategies, whether it’s adjusting your pricing, launching new products, or enhancing customer service.
- Intermediaries: Partnering with reliable intermediaries can streamline logistics and payment processing, reducing friction points in the customer journey.
- Media: Proactive media management helps build a positive brand image, making your e-commerce store the go-to choice for customers.
In contrast, failing to address these factors can lead to stockouts, lost customers, and a damaged reputation. The micro environment is where your day-to-day success is forged. But what about macro environment factors?
What Are Macro Environment Factors?
Unlike micro environment factors, which businesses can control or directly influence, macro environment factors are the larger, external forces that shape the entire e-commerce industry. These include economic shifts, technological advancements, legal regulations, and societal changes that can either create opportunities or pose threats to e-commerce businesses. Understanding these factors is crucial for strategic planning, as they often dictate market trends and consumer behaviors that no single company can alter but must adapt to.
List of Key External Factors Affecting E-Commerce
- Economic Environment: The Pulse of Consumer Spending. The economic landscape plays a significant role in shaping consumer behavior. Factors like inflation, interest rates, and overall economic health influence how much consumers are willing to spend.
- Technological Factors: Riding the Wave of Innovation. The rapid pace of technological change is a defining feature of the macro environment. Emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, and mobile commerce are transforming the e-commerce landscape by enhancing customer experiences and streamlining operations.
- Legal and Regulatory Factors: Navigating the Compliance Minefield. The legal environment is a crucial macro factor that affects e-commerce operations globally. Regulations related to data privacy (like GDPR in the EU) and consumer protection laws dictate how businesses must handle customer data and advertising practices.
- Social and Cultural Factors: Aligning with Changing Consumer Values. Social and cultural trends have a profound impact on e-commerce. Shifts in consumer behavior, such as the rise of ethical shopping and demand for sustainable products, are reshaping the market.
- Environmental Factors: Adapting to Sustainability Demands. As awareness of climate change and environmental issues grows, so does the importance of eco-friendly practices in e-commerce. Consumers are becoming more selective, favoring companies that demonstrate sustainable operations and minimize their carbon footprint.
- Political Factors: The Impact of Government Policy and Stability. Political stability, trade policies, and international relations significantly influence cross-border e-commerce.
US elections in 2024 are associated with political uncertainty and instability which is a macro environment factor
Impact of Macro Environment on E-Commerce
External factors play a pivotal role in shaping the long-term strategies of e-commerce businesses. Here’s how these external forces can affect decision-making:
- Economic Shifts: During inflationary periods, companies might need to introduce lower-priced alternatives or special promotions to maintain sales volumes because shoppers might prioritize essential goods and look for discounts, directly affecting sales for luxury e-commerce brands.
- Technological Advances: AI-driven product recommendations can significantly increase sales, while blockchain technology ensures secure and transparent transactions. Adopting them can help businesses personalize the shopping experience and make it more secure, boosting customer satisfaction and conversion rates.
- Legal Compliance: Keeping up with changing regulations like data privacy laws ensures smooth operations and maintains consumer trust. Failing to comply with them can lead to hefty fines and lost customer trust.
- Social Changes: Responding to trends like ethical shopping can open up new customer segments and drive brand loyalty. Younger generations, for instance, increasingly prefer to buy from brands that align with their values, such as those that prioritize sustainability or social justice.
- Environmental Pressures: Brands that use recyclable packaging or offset their emissions tend to attract eco-conscious shoppers. Investing in sustainable practices not only appeals to eco-conscious consumers but also helps future-proof the business against tightening regulations.
- Political Instability: Changes in trade agreements or tariffs can impact the cost of importing goods, while political instability in certain regions may disrupt supply chains. The recent US-China trade tensions serve as a prime example, where shifts in tariff policies affected the pricing and availability of products on major e-commerce platforms. So, diversifying supply chains and adapting to new trade policies can help businesses mitigate the risks associated with political uncertainty.
Since macro environment factors shape the broader landscape of e-commerce, businesses need to stay informed and agile — turning external challenges into opportunities for growth and innovation.
Key Differences Between Internal and External Factors

Understanding the distinction between micro environment factors and macro environment factors is crucial for shaping effective business strategies in e-commerce. While both types of factors influence the way a business operates, their impact and the level of control a company has over them differ significantly.
1. Level of Control: Internal vs. External Forces
Micro environment factors are the elements that businesses can often control or directly influence. These include internal aspects like customer relationships, supplier agreements, and marketing tactics. For example, an e-commerce retailer like Amazon can fine-tune its pricing strategy, negotiate better deals with suppliers, or adjust its product offerings based on customer feedback. In this sense, micro factors allow for quick, tactical responses.
On the other hand, macro environment factors exist outside the company’s immediate control. These external forces — such as economic downturns, changes in technology, or new regulations — require businesses to adapt rather than control. Take the COVID-19 pandemic as an example: it disrupted global supply chains and altered consumer behavior on a massive scale. Companies had to pivot their strategies, shifting from physical retail to online sales and adjusting to new consumer demands for essential goods and contactless delivery options.
2. Impact on Strategy: Tactical Adjustments vs. Long-Term Planning
Internal factors directly influence tactical decisions. They affect the day-to-day operations of an e-commerce business, requiring frequent adjustments to meet immediate goals. For instance, if a key supplier faces delays, a business might need to adjust its inventory levels or switch to an alternative supplier quickly to avoid stockouts. Similarly, monitoring customer feedback allows companies to tweak their marketing campaigns or improve product features on the fly.
In contrast, external factors affecting business play a critical role in long-term strategic planning. These broader trends and forces often dictate the overall direction of the company. For example, the growing emphasis on data privacy and regulations like GDPR has pushed e-commerce companies to invest heavily in data protection measures. Rather than making small adjustments, businesses need to adapt their entire framework, integrating compliance into their core operations and technology stack to avoid legal repercussions and build consumer trust.
Examples in E-Commerce: Case Studies Highlighting the Differences
Let’s dive into some real-world examples to illustrate how micro and macro environment factors shape the strategic decisions of e-commerce giants like Amazon.
- Micro Environment Response: Supplier Issues at Amazon. In 2019, Amazon faced challenges with certain suppliers who were unable to meet demand during the holiday season. Amazon swiftly adjusted its inventory strategy, prioritizing products from alternative suppliers and leveraging its extensive logistics network to keep up with consumer demand. This quick, tactical response showcases how businesses can maneuver around internal factors to maintain operational efficiency.
- Macro Environment Adaptation: New Privacy Regulations. In response to the introduction of GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the European Union, Amazon had to overhaul its data handling practices across its entire platform. This wasn’t a simple adjustment — it required a complete revamp of how customer data was collected, stored, and processed. The change was driven by a external factor affecting business, forcing Amazon to align its long-term strategy with the new legal requirements to avoid fines and maintain customer trust.
Summary of Key Differences
| Aspect | Micro Environment Factors | Macro Environment Factors |
| Control | Controllable and direct influence | Beyond the company’s direct control |
| Focus | Tactical, short-term adjustments | Strategic, long-term planning |
| Response | Quick, reactive measures | Proactive, adaptive strategies |
| Examples | Supplier negotiations, customer feedback responses | Economic shifts, regulatory changes |
In essence, micro environment factors allow businesses to react and make immediate changes, optimizing their current operations. Meanwhile, macro environment factors shape the bigger picture, forcing companies to adapt their overall strategy to align with external trends and forces. Understanding both is essential for a balanced e-commerce strategy; overlooking either one can leave your business exposed to unexpected risks and missed opportunities.
SWOT Analysis for Micro and Macro Environment Factors

Conducting a SWOT analysis helps e-commerce businesses identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats posed by both micro environment factors and macro environment factors. By understanding these dynamics, companies can make informed decisions that optimize their operations and strategically prepare for future challenges.
Table 1: Micro Environment Factors (SWOT Analysis)
| Micro Environment Factors | Description |
| Strengths | Strong customer relationships, reliable suppliers, and agile marketing strategies. E-commerce businesses can leverage direct interactions with customers to gather feedback and quickly adapt their offerings. Solid partnerships with logistics and payment intermediaries also enhance service quality and customer satisfaction. |
| Weaknesses | Over-reliance on a single supplier, limited differentiation from competitors, and potential negative media coverage. When a business depends heavily on one supplier, any disruption can halt operations. Additionally, poor public perception or negative reviews can damage brand’s reputation quickly. |
| Opportunities | Expanding into new customer segments, forming partnerships with innovative third-party services, and enhancing personalization strategies. For instance, integrating AI-driven recommendations can open up new sales channels and improve conversion rates. Strategic collaborations with emerging logistics providers can also streamline order fulfillment. |
| Threats | Aggressive competitor tactics, price wars, and supply chain disruptions. In a highly competitive market, rivals might undercut prices or launch exclusive products, putting pressure on smaller e-commerce businesses. Disruptions in the supply chain, whether due to natural disasters or logistical issues, can also lead to stockouts and lost sales. |
Table 2: Macro Environment Factors (SWOT Analysis)
| Macro Environment Factors | Description |
| Strengths | Economic growth, favorable technological advancements, and a stable regulatory environment. A strong economy boosts consumer spending while emerging technologies like mobile commerce and AI enhance operational efficiency. A stable legal framework can also provide a predictable business environment, helping e-commerce companies plan strategically. |
| Weaknesses | Limited adaptability to sudden changes in regulations, exposure to volatile economic conditions, and dependency on global supply chains. Rapid shifts in legal requirements, like new data protection laws, may force companies to overhaul their processes at significant cost. Additionally, economic downturns can reduce consumer spending power, affecting sales across the board. |
| Opportunities | Expansion into emerging markets, capitalizing on green consumer trends, and leveraging government incentives. E-commerce companies that enter developing regions can tap into new customer bases while embracing sustainable practices can attract eco-conscious shoppers. Government support for digital transformation initiatives may also provide financial incentives for technology upgrades. |
| Threats | Economic recessions, changing legal requirements, and political instability. During economic downturns, reduced consumer spending can negatively impact sales, especially for non-essential items. Shifts in trade policies or political uncertainty can disrupt cross-border operations and lead to increased costs. Additionally, tightening environmental regulations might force businesses to adopt more costly sustainable practices. |
As you can see, internal factors are more controllable and allow for direct tactical responses, making them ideal for short-term adjustments to improve customer satisfaction, optimize supply chains, and react to competitor actions.
external factors, on the other hand, require a more strategic approach, as they shape the larger context in which businesses operate. By identifying opportunities in emerging markets and staying ahead of technological trends, companies can build resilience against economic volatility and regulatory changes.
Mitigating the Impact of Micro and Macro Environment Factors in E-Commerce
Navigating the complexities of micro environment factors and macro environment factors is essential for e-commerce businesses aiming to thrive in a competitive landscape. Proactive strategies can help leverage the positives while minimizing potential drawbacks. Let’s explore effective approaches for managing both types of factors.
Micro Environment Mitigation Strategies
When it comes to micro environment factors affecting business, a hands-on approach is vital. Since these elements are within a company’s direct control, businesses can make quick adjustments to optimize outcomes.
- Leverage Positive Factors: Strengthen What Works
- Optimize Supply Chain Efficiency: Strengthen relationships with key suppliers to ensure consistent product availability. Using just-in-time inventory systems can help reduce holding costs and streamline operations.
- Enhance Customer Engagement: Invest in tools that personalize the shopping experience, such as AI-driven recommendations and chatbots for real-time customer support. This not only boosts sales but also builds long-term brand loyalty.
- Build Stronger Brand Loyalty: Create a robust loyalty program that rewards repeat customers. For example, Sephora’s Beauty Insider program has been instrumental in retaining customers by offering personalized perks and exclusive access.
- Mitigate Negative Factors: Be Prepared for Disruptions
- Diversify Supplier Networks: Don’t rely too heavily on a single supplier. Instead, build a diverse network of partners to avoid disruptions. If one supplier faces delays, having backup options can keep your business running smoothly.
- Implement Competitive Pricing Strategies: Regularly monitor competitors’ prices and adjust your own pricing strategy accordingly. Utilizing dynamic pricing tools can help you stay competitive while maximizing profit margins.
- Utilize Real-Time Customer Feedback: Actively gather and analyze customer feedback to identify areas for improvement. Platforms like Trustpilot and Google Reviews provide valuable insights that can help refine your product offerings and service quality.
Macro Environment Mitigation Strategies
Adapting to macro environment factors affecting business requires a broader, strategic outlook. These external forces are beyond direct control, but businesses can still position themselves advantageously by anticipating changes and preparing accordingly.
- Leverage Positive Trends: Capitalize on Market Shifts
- Stay Ahead of Technology Trends: Invest in emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, and augmented reality (AR). For example, AR tools like virtual try-ons have become game-changers in the fashion and beauty industries, driving engagement and reducing return rates.
- Expand into Favorable Economic Regions: Look for growth opportunities in emerging markets where e-commerce penetration is increasing. Regions like Southeast Asia and Latin America are experiencing rapid digital adoption, offering untapped customer bases.
- Adapt Quickly to Social Trends: Pay attention to shifts in consumer behavior, such as the rising demand for eco-friendly products. Aligning your product offerings with these trends can help attract socially conscious shoppers and enhance your brand reputation.
- Mitigate Negative Factors: Prepare for the Unexpected
- Develop Contingency Plans for Economic Downturns: Build financial resilience by diversifying your product range and focusing on essentials during economic slumps. Consider offering flexible payment options like “buy now, pay later” to cater to budget-conscious consumers.
- Stay Compliant with Changing Regulations: Keep abreast of new legal requirements, especially in areas like data privacy and consumer protection. Investing in compliance software can help automate regulatory updates and ensure your business remains on the right side of the law.
- Engage in Sustainable Practices: With increasing environmental awareness, businesses must embrace sustainability to meet consumer expectations and regulatory demands. Implement practices like reducing packaging waste and using eco-friendly shipping options. For instance, companies like Patagonia have built strong brand loyalty by prioritizing environmental sustainability.
Now, you can see that a proactive approach to both micro and macro environment factors can help e-commerce companies turn potential threats into opportunities, positioning themselves for sustained growth in an ever-evolving market.
Understanding both micro environment factors and macro environment factors is not just beneficial — it’s essential for long-term success. While internal factors affecting business can be controlled through agile, tactical responses, the broader external factors require a strategic mindset and the flexibility to adapt to external changes.
The key takeaway for e-commerce businesses? Monitor both environments continuously. By keeping a pulse on internal elements like customer feedback and supplier performance, companies can fine-tune their operations and stay competitive. At the same time, staying aware of macro environment factors, such as economic shifts, regulatory changes, and technological trends, helps organizations anticipate challenges and seize new opportunities.
Proactive management is the secret sauce. E-commerce leaders who embrace change, leverage data for informed decisions, and quickly adapt their strategies will survive and thrive in a landscape shaped by constant evolution. In an industry where consumer expectations are rising and market dynamics are shifting rapidly, those who understand and act on these factors will set the pace, not just keep up with it.
The bottom line? The best defense against uncertainty is a strong offense: a well-rounded, adaptive approach that turns micro and macro factors into powerful growth drivers.