Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Explained: How to Calculate and Improve It

In today’s competitive market, businesses can no longer rely on one-time purchases to stay profitable. Instead, Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) has become a key metric for long-term growth, helping brands understand the total revenue a customer is expected to generate throughout their relationship with a company. But what is CLV exactly, and why does it matter?
Customer Lifetime Value measures how much profit a business can earn from a single customer over time. By focusing on CLV, companies can refine their marketing strategies, improve customer retention, and make data-driven decisions to maximize profitability. Understanding and calculating customer lifetime value allows businesses to shift from short-term gains to sustainable revenue growth.
In this guide, we’ll break down what customer lifetime value is, how to calculate CLV using different formulas, and strategies to improve it. Whether you’re running an e-commerce store, SaaS business, or a subscription service, mastering CLV can give you a competitive edge.

Table of contents
- What Is Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)?
- Key Benefits of Calculating CLV for Business Growth
- How to Calculate Customer Lifetime Value
- How to Improve Your CLV Calculation Accuracy
- What to Do Next: Turning CLV Insights into Actionable Strategies
- Common Mistakes in Applying Customer Lifetime Value – And How to Avoid Them
- How to Increase Your Customer Lifetime Value and Maximize Long-Term Revenue
- FAQ: Customer Lifetime Value Explained
What Is Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)?
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is a business metric that estimates the total revenue a company can expect from a single customer throughout their relationship. In simple terms, CLV helps businesses understand how valuable a customer is beyond just one purchase. The formal definition describes CLV as the present value of future cash flows generated by a customer, considering their purchasing behavior, retention rate, and average transaction value.
Why does knowing your customer lifetime value matter? CLV helps businesses make smarter marketing and budget decisions by determining how much they can afford to spend on acquiring and retaining customers. For instance, if the CLV of an average customer is $1,000 and it costs $150 to acquire them, that’s a profitable investment. But if acquisition costs exceed CLV, the business needs to rethink its marketing strategy.
CLV is especially valuable for relationship-driven industries, such as banking, insurance, SaaS, and telecommunications, where long-term customer retention is key. However, e-commerce and retail businesses also benefit from CLV insights. Take two different business models:
- A luxury fashion brand targeting high-net-worth customers may use a short-term CLV model, as their clients make expensive but infrequent purchases.
- A subscription-based meal delivery service relies on a long-term CLV model, as customers make frequent, lower-cost purchases over time.
Understanding how to calculate customer lifetime value allows businesses to identify their most profitable customers, refine marketing campaigns, and develop strategies to increase customer retention and profitability.
Key Benefits of Calculating CLV for Business Growth
While Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) may seem complex at first, its long-term benefits for business growth and profitability make it an essential metric. By understanding how much revenue a customer generates over time, businesses can make smarter marketing investments, optimize customer retention strategies, and maximize ROI.
1️⃣ Stronger Long-Term Customer Relationships
CLV helps businesses shift from short-term sales tactics to long-term relationship-building. Instead of chasing one-time buyers, companies can focus on engaging, retaining, and upselling to high-value customers.
🔹 Example: Subscription-based brands like Netflix and Spotify prioritize customer engagement and personalization to keep users subscribed, increasing their CLV over time.
2️⃣ Optimized Marketing Spend & ROI
Knowing how much a customer is worth allows businesses to allocate their marketing budget efficiently. Companies can determine how much to spend on customer acquisition while ensuring they maintain a profitable return on investment (ROI).
🔹 Example: If an e-commerce brand discovers that social media ads attract high-CLV customers, they can increase investment in that channel while reducing spend on less effective ones.
3️⃣ Data-Driven Decision-Making
CLV allows businesses to predict the financial impact of different marketing and customer management strategies. By analyzing CLV trends, companies can adjust their pricing models, promotions, and customer retention efforts accordingly.
🔹 Example: A SaaS company might use CLV data to determine whether offering a 14-day free trial leads to higher retention rates and increased CLV compared to a 7-day trial.
4️⃣ More Effective Advertising Strategies
Instead of casting a wide net, businesses can target ads toward customers with the highest potential lifetime value. This reduces acquisition costs and ensures ad spend is directed at profitable customer segments.
🔹 Example: High-end fashion retailers prioritize high-income customers who are likely to make repeated luxury purchases, rather than spending on audiences who only buy during sales.
5️⃣ Shifts Focus from Short-Term Gains to Long-Term Profitability
Many businesses waste money acquiring “cheap” or low-value customers who don’t return. CLV encourages a strategic shift toward retaining high-value customers, which is more cost-effective than constantly chasing new buyers.
🔹 Fact: Studies show that the probability of selling to an existing customer is 60-70%, while selling to a new customer is only 5-20%. Retaining customers is 5X cheaper than acquiring new ones.
6️⃣ Better Resource Allocation Across Business Functions
CLV helps businesses distribute resources efficiently, ensuring marketing, sales, and customer support teams focus on maximizing long-term value rather than short-term transactions.
🔹 Example: A SaaS company might allocate more resources to customer success teams to improve retention and reduce churn, rather than spending aggressively on new user acquisition.
7️⃣ Identifies the Most Valuable Customer Segments
By analyzing CLV data, businesses can determine which customer demographics, behaviors, and purchasing habits contribute the most revenue. This enables hyper-targeted marketing and loyalty programs.
🔹 Example: Amazon optimizes its Prime membership program based on CLV insights, ensuring loyal customers receive exclusive benefits that keep them engaged.
8️⃣ Measures Customer Loyalty & Retention Success
CLV is a great indicator of customer loyalty. Businesses with high CLV metrics typically have strong retention strategies, leading to sustainable revenue growth and lower acquisition costs.
🔹 Example: Companies like Apple and Starbucks consistently increase customer lifetime value through brand loyalty programs, seamless user experiences, and product ecosystems.
How to Calculate Customer Lifetime Value
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is a forward-looking metric, meaning it requires businesses to estimate future transactions, retention rates, and spending habits. Because predicting future customer behavior involves uncertainty, calculating CLV can seem complex—but with the right approach, businesses can use CLV to make smarter marketing and financial decisions.
Key Factors in CLV Calculation
To accurately calculate customer lifetime value, businesses typically consider the following factors:
- Customer lifespan — How long, on average, a customer continues purchasing from the business.
- Average order value (AOV) — The average amount a customer spends per transaction.
- Purchase frequency — How often a customer buys within a given time period.
- Profit margin — The percentage of revenue that remains after costs.
- Retention rate & churn rate — The likelihood that a customer will continue doing business with you.
- Discount rate — The time value of money, which accounts for future revenue being less valuable than present revenue.
Choosing the Right CLV Calculation Model
Businesses can choose between simple CLV formulas for quick estimates and advanced models for precise forecasting. The key trade-offs when picking a model are accuracy, complexity, and cost.
1. Basic CLV Formula: A Quick and Simple Approach
For businesses looking for a fast and straightforward way to estimate CLV, this basic formula works well:
![]()
Where:
- AOV (Average Order Value) = Total Revenue ÷ Total Orders
- Purchase Frequency = Total Orders ÷ Total Customers
- Customer Lifespan = Average number of years a customer stays with the company
🔹 Example: If a coffee subscription company has an AOV of $20, customers order twice per month, and the average customer stays 3 years, the CLV would be:
![]()
This means the average customer is worth $1,440 over their lifetime.
🟢 Pros: Easy to calculate, good for a rough estimate.
🔴 Cons: Doesn’t factor in retention rate, churn, or discount rates, making it less accurate for long-term planning.
2. Discounted CLV Formula: More Accurate for Long-Term Planning
For businesses with recurring revenue models, such as SaaS or subscription-based services, a more accurate approach involves factoring in profit margin, retention rate, and discount rate:
![]()
🔹 Example: Imagine a SaaS business has:
- A monthly profit per customer of $50
- A retention rate of 85% (0.85)
- A discount rate of 10% (0.10)
Using the formula:
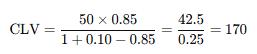
So, the projected CLV per customer is $170 per month.
🟢 Pros: More realistic, accounts for retention and the diminishing value of future revenue.
🔴 Cons: Requires more data and assumes constant retention rates.
3. Advanced CLV Models for High-Accuracy Predictions
For enterprises looking for the most accurate CLV predictions, advanced models incorporate customer segmentation, behavioral analytics, and machine learning algorithms.
✔️ Google Analytics CLV Calculation
- Businesses can track CLV using Google Analytics, by importing transactional data and segmenting customer cohorts.
- Measurement Protocol helps capture purchase data directly, while Dimension Widening allows detailed segmentation.
✔️ Kissmetrics CLV Example: Starbucks Case Study
- Starbucks calculates CLV using a custom formula that factors in:
- Purchase frequency (times per week)
- Average spend per visit
- Customer lifespan (years)
- The company determines high-value vs. low-value customers, refining loyalty programs accordingly.
✔️ CLV Calculators & Tools
For businesses aiming to automate Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) calculations, several contemporary tools offer real-time insights and predictive analytics:
- : A Relationship Marketing software that combines a Customer Data Platform with algorithmic optimization to autonomously enhance multichannel campaigns. Optimove caters to industries such as retail, e-commerce, travel, gaming, and financial services.
- : This online tool allows businesses to quickly compute CLV by inputting metrics like average purchase value, purchase frequency, and customer lifespan. It’s designed for ease of use, providing immediate estimates to inform marketing strategies.
- : Mosaic offers a straightforward calculator that helps businesses determine CLV by considering factors such as average revenue per user (ARPU), gross margin, and churn rate. This tool aids in understanding the long-term value of customers to optimize acquisition and retention efforts.
- : Qualtrics provides a user-friendly calculator that estimates CLV by multiplying customer value by the average customer lifespan. This tool assists businesses in making informed decisions regarding customer acquisition costs and marketing investments.
- : WebFX offers an online tool that calculates CLV by subtracting the cost of acquiring a customer from the revenue generated over their lifetime. This calculator helps businesses assess the profitability of their customer relationships.
These tools cater to various business needs, from simple online calculators for quick estimates to comprehensive platforms offering in-depth predictive analytics. Selecting the appropriate tool depends on your organization’s specific requirements and the complexity of your customer data.
How to Improve Your CLV Calculation Accuracy
Accurately calculating Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is critical for businesses looking to optimize marketing budgets, improve retention, and maximize long-term profitability. However, inaccurate or incomplete CLV calculations can lead to misleading insights and poor decision-making. By refining how you track and analyze CLV, businesses can make data-driven decisions that lead to sustainable growth.
Key Strategies to Enhance CLV Accuracy
- Use Cohort Analysis to Track Customer Behavior Over Time
Instead of treating all customers the same, cohort analysis groups them based on shared characteristics—such as acquisition date, purchase behavior, or subscription tier. This approach reveals trends in repeat purchases, retention rates, and spending habits, allowing businesses to refine CLV models more effectively.
🔹 Example: An online fashion retailer can segment customers who made their first purchase during a seasonal sale vs. regular-priced buyers. If the discount-driven cohort has a shorter lifespan, the brand might adjust future discount strategies to attract more loyal shoppers. - Monitor Retention & Churn Rates Dynamically
Since CLV is directly tied to customer retention, tracking churn rate (customers who stop buying) and retention rate (customers who continue purchasing) helps adjust CLV calculations in real time. Companies should regularly update their retention metrics to reflect current market conditions.
🔹 Example: A SaaS company offering a monthly subscription service notices a sudden increase in churn rate. By analyzing customer feedback, they identify poor customer support as a key issue. Addressing this problem leads to improved retention, increasing overall CLV. - Segment Customers by High-Value vs. Low-Value Spenders
Not all customers contribute equally to revenue. By identifying high-value customers (HVCs) vs. low-value customers (LVCs), businesses can refine CLV projections and focus resources on the most profitable segments.
🔹 Example: Amazon Prime members have a CLV exceeding $2,500, compared to the average e-commerce CLV of $168. By investing in Prime-exclusive perks and fast shipping, Amazon increases customer stickiness and long-term profitability. - Consider Industry Benchmarks to Compare CLV with Competitors
Benchmarking CLV against competitors helps businesses evaluate performance and set realistic growth targets. Different industries have varying CLV expectations, so understanding where your business stands in comparison can inform pricing, loyalty programs, and marketing efforts.
🔹 Example:- E-commerce CLV benchmark: ~$168 per customer
- SaaS (Subscription) CLV benchmark: Depends on Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) and retention
- Streaming services (e.g., Netflix, Spotify): Focus on high engagement to increase long-term CLV
Leverage CLV Tools for Accurate Calculation
For businesses seeking automation, advanced CLV calculation tools help analyze data and provide predictive insights. Some of the most effective tools include:
- Optimove – AI-powered predictive analytics for CLV modeling
- Google Analytics CLV Reports – Tracks CLV for different customer segments
- Mosaic CLV Calculator – Provides financial insights using gross margin and retention metrics
- WebFX CLV Calculator – Simple tool for estimating CLV quickly
- Qualtrics CLV Analysis – Helps businesses measure and optimize CLV with customer experience data
Mastering how to calculate Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) accurately allows businesses to make informed investment decisions in marketing, sales, and retention strategies. Whether through cohort analysis, segmentation, or industry benchmarking, refining CLV calculations ensures businesses can maximize profitability and long-term customer relationships.
💡 Take Action: Start by evaluating your current CLV model, tracking retention trends, and testing different customer segmentation strategies to enhance accuracy and grow revenue.
What to Do Next: Turning CLV Insights into Actionable Strategies
Once you’ve calculated your average Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), the next step is to segment your customers to identify the most valuable ones. Not all customers contribute equally to revenue — some bring in consistent, long-term value, while others may only make one-time purchases. By segmenting customers based on key factors, businesses can optimize marketing, retention, and acquisition strategies to maximize profitability.
Key customer segmentation strategies based on CLV are:
1. Segment Customers by Acquisition Source
Understanding where your high-value customers come from helps businesses allocate marketing budgets effectively. Different acquisition channels—such as organic search, paid ads, social media, and referral programs—can lead to vastly different CLV figures.
🔹 Example:
- A DTC (direct-to-consumer) beauty brand discovers that customers who found them via Instagram ads have a 50% higher CLV than those acquired through Google Ads.
- A SaaS company finds that organic search traffic generates more long-term paying subscribers than Facebook retargeting ads.
💡 Actionable Insight: If a particular channel attracts higher-value customers, increase investment in that channel while cutting costs on lower-performing ones.
2. Segment Customers by Demographics
Demographics like age, gender, location, and income level can reveal who your most valuable customers are and help fine-tune targeting.
🔹 Example:
- A fitness subscription service finds that millennials (ages 25-34) have a 40% higher CLV than older age groups, leading them to tailor content and promotions specifically for this audience.
- A luxury watch brand discovers that high-income male customers from the U.S. have the highest CLV, guiding their ad spend toward premium platforms and influencers.
💡 Actionable Insight: Adjust your ad creatives, messaging, and pricing strategies based on the demographics that yield the highest long-term revenue.
3. Identify High-Value vs. Low-Value Customers
Not all customers are equally profitable—some spend consistently, while others make a few low-value purchases and never return.
🔹 Example:
- Amazon Prime members have a CLV of over $2,500, compared to non-members with an average CLV of $168. As a result, Amazon prioritizes Prime membership perks to increase customer loyalty.
- Subscription businesses like Netflix & Spotify focus on reducing churn because even a 1% increase in retention can significantly boost overall CLV.
💡 Actionable Insight: Create personalized marketing and loyalty programs for your high-value customers, offering exclusive deals, early access, or VIP perks.
4. Optimize Retention Strategies Based on CLV Segmentation
Once you’ve identified your most valuable customer segments, focus on keeping them engaged for as long as possible.
✅ For high-CLV customers:
- Exclusive loyalty programs (e.g., Sephora’s Beauty Insider or Starbucks Rewards)
- Personalized promotions based on past purchases
- Subscription-based incentives (discounted annual memberships, early access to new products)
✅ For low-CLV customers:
- Win-back email campaigns with targeted offers
- Onboarding improvements to boost first-purchase engagement
- Re-engagement ads for inactive users
Understanding Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) isn’t just about calculations — it’s about making smart business decisions that drive long-term profitability. By segmenting customers based on acquisition source, demographics, and spending behavior, businesses can fine-tune marketing strategies, reduce acquisition costs, and maximize revenue per customer.
💡 Next Steps:
✔ Reevaluate your marketing spend based on high-CLV acquisition channels.
✔ Adjust messaging and targeting to focus on your most profitable customer demographics.
✔ Invest in retention programs that keep high-value customers engaged for longer.
By applying CLV-driven strategies, businesses can scale more efficiently, reduce wasted ad spend, and improve overall profitability — ensuring every marketing dollar is well spent.
Common Mistakes in Applying Customer Lifetime Value – And How to Avoid Them
While Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is a powerful metric for understanding customer profitability, many businesses misinterpret or misuse CLV data, leading to flawed decision-making. These mistakes can result in misallocated budgets, ineffective marketing strategies, and missed revenue opportunities. Below are some of the most common CLV pitfalls and how to avoid them.
1. Misidentifying “Unprofitable” Customers
One of the biggest misconceptions businesses have is that customers who generate low revenue are unprofitable and should be ignored. While they may not seem valuable at first glance, these customers can contribute to brand awareness, referrals, and incremental sales over time.
🔹 Example:
- Freemium SaaS models (e.g., Spotify, Dropbox) rely on free-tier users to build brand loyalty and upsell premium plans later.
- E-commerce businesses often see low-value buyers evolve into high-value customers when nurtured through loyalty programs, retargeting, and personalized marketing.
💡 Fix: Instead of ignoring low-value customers, segment them and analyze whether they have the potential to increase their spending over time through targeted engagement strategies.
2. Confusing Revenue with Net Profit
Many businesses mistakenly equate revenue with profit, which leads to overestimating CLV and making poor financial decisions. Revenue only represents total income, while net profit accounts for acquisition costs, operational expenses, and other deductions.
🔹 Example:
- A subscription box company sees an average revenue per customer of $500, but after considering marketing, shipping, and customer service costs, the actual profit per customer is only $150. Overestimating CLV based on revenue alone can lead to excessive spending on customer acquisition.
💡 Fix: When calculating customer lifetime value, always factor in costs such as:
✔ Customer acquisition costs (CAC)
✔ Operational and fulfillment costs
✔ Discounts and returns
✔ Customer service expenses
Use the profit-based CLV formula:
![]()
This gives a more accurate measure of actual customer profitability.
3. Relying on Intuition Instead of Data-Driven Insights
Some businesses underestimate CLV and make marketing decisions based on gut feelings or demographic assumptions rather than actual data. This can lead to misallocating budgets toward the wrong customer segments.
🔹 Example:
- A fashion retailer assumes that their biggest spenders are middle-aged men based on intuition. However, CLV analysis shows that younger female customers generate higher long-term revenue due to repeat purchases and brand loyalty.
💡 Fix: Instead of guessing which customers are the most valuable, businesses should use:
✔ Cohort analysis to track purchasing behavior over time
✔ CLV segmentation to group customers by profitability
✔ Predictive analytics tools (e.g., Google Analytics, Optimove) to refine marketing strategies
4. Overlooking the Importance of Customer Retention
Some businesses focus too much on acquiring new customers while neglecting customer retention strategies, leading to a lower overall CLV. Research shows that increasing customer retention by just 5% can boost profits by 25-95%.
🔹 Example:
- A DTC skincare brand invests heavily in paid ads to acquire new customers but fails to implement loyalty programs or email remarketing. As a result, most buyers purchase once and never return, decreasing overall CLV.
💡 Fix: Instead of constantly chasing new customers, businesses should:
✔ Implement personalized loyalty programs (e.g., Sephora’s Beauty Insider)
✔ Use email retargeting & post-purchase follow-ups
✔ Improve customer service to boost satisfaction and retention
5. Assuming CLV Models Are Always Accurate
Many CLV models rely on historical data and assumptions, which can lead to miscalculations if customer behavior changes over time. CLV projections don’t always account for external factors, such as:
- Market shifts (e.g., economic downturns, inflation)
- Competitor pricing strategies
- Changing consumer preferences
🔹 Example:
- A fitness app calculates a CLV of $500 per user based on past behavior, but fails to account for a growing trend of free workout content on YouTube, leading to lower retention rates than expected.
💡 Fix: Instead of treating CLV as a fixed number, businesses should regularly update CLV models based on:
✔ Changing customer retention trends
✔ Seasonality & external market factors
✔ New product launches or competitive pricing changes
6. Failing to Use CLV Insights to Optimize Marketing Strategies
Some companies calculate CLV but fail to apply it effectively in their marketing and retention strategies. Simply knowing your CLV is useless if you don’t adjust your business strategy based on the insights.
🔹 Example:
- A meal kit subscription service discovers that customers acquired via YouTube influencers have a higher CLV than those from Facebook ads. However, they continue spending equally across all channels, missing out on higher ROI from influencer marketing.
💡 Fix: Businesses should apply CLV insights to:
✔ Refine ad spend allocation (focus on high-CLV acquisition channels)
✔ Create tailored loyalty programs for high-value customers
✔ Adjust pricing, promotions, and customer service strategies to boost retention
How to Increase Your Customer Lifetime Value and Maximize Long-Term Revenue
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is one of the most important metrics for businesses looking to increase profitability and customer retention. The higher your CLV, the more revenue your business generates from each customer over time. But how do you effectively increase CLV? The key lies in enhancing customer experience, encouraging repeat purchases, and building long-term relationships.
Below are proven strategies to boost customer lifetime value and ensure customers keep coming back.
1️⃣ Provide Exceptional Customer Support and Instant Assistance
Customers stay loyal to brands that prioritize their needs and provide instant solutions. If they feel valued and supported, they are more likely to make repeat purchases and recommend your brand.
🔹 Example:
- Amazon’s 24/7 customer service and hassle-free returns policy contribute to its high CLV and customer retention rates.
- Live chat, chatbots, and AI-driven assistants can reduce cart abandonment by up to 30% by solving issues in real-time.
💡 Actionable Tip: Implement live chat support, AI chatbots, and email follow-ups to assist customers before they abandon their purchase.
2️⃣ Nurture Customers with Personalized Emails & Discounts
Regular engagement with customers through personalized email marketing, product recommendations, and exclusive discounts keeps them engaged and more likely to return.
🔹 Example:
- Sephora’s Beauty Insider program sends tailored emails based on customer preferences and purchase history, increasing their average order value (AOV).
- Spotify’s Discover Weekly playlist keeps users engaged, increasing subscription renewal rates and boosting CLV.
💡 Actionable Tip: Send personalized discount offers, abandoned cart reminders, and product recommendations based on past purchases.
3️⃣ Retarget Customers Who Haven’t Purchased Yet
Not every visitor to your store will buy right away. Some may return later when they’re ready, while others may need a small nudge to complete a purchase.
🔹 Example:
- Facebook & Google retargeting ads can re-engage visitors who browsed your site but didn’t complete a purchase.
- Brands like Nike and Adidas use dynamic remarketing ads to show customers the exact products they previously viewed, leading to higher conversion rates.
💡 Actionable Tip: Use retargeting campaigns to bring back potential buyers with personalized offers or free shipping incentives.
4️⃣ Strengthen Customer Loyalty with Personalization & Shared Values
Customers stay loyal to brands that share their values and make them feel connected. A personalized shopping experience makes customers feel appreciated and encourages repeat business.
🔹 Example:
- Patagonia’s eco-friendly mission attracts loyal customers who align with the brand’s sustainability goals.
- Netflix personalizes recommendations, making subscribers less likely to cancel their memberships.
💡 Actionable Tip: Show customers you care about their values by personalizing offers and aligning your brand with social causes that resonate with them.
5️⃣ Track and Recalculate Your CLV Regularly
CLV is not a static number—it changes based on customer behavior, retention rates, and business strategies. Regularly tracking CLV allows businesses to adjust their approach and optimize profitability.
🔹 Example:
- A SaaS business tracks CLV monthly and notices that retention drops after three months. They introduce a retention campaign, reducing churn by 15% and boosting overall CLV.
💡 Actionable Tip: Recalculate CLV at least once a month to measure the impact of new marketing and retention strategies.
6️⃣ Optimize Purchase Frequency & Increase AOV
Since CLV is directly influenced by purchase frequency and AOV, businesses must actively encourage repeat purchases and upsells.
🔹 Example:
- McDonald’s meal combo strategy increases AOV by bundling fries, drinks, and burgers together.
- Amazon’s “Frequently Bought Together” feature encourages multi-product purchases, boosting overall revenue.
💡 Actionable Tip: Offer product bundles, upsells, and loyalty discounts to increase AOV and purchase frequency.
7️⃣ Identify and Focus on High-Value Customer Sources
Some acquisition channels bring in more valuable customers than others. Tracking which marketing sources generate high-CLV customers allows businesses to optimize ad spend for maximum returns.
🔹 Example:
- A luxury fashion brand finds that customers acquired through influencer marketing have 50% higher CLV than those from Google Ads.
- Apple’s CLV strategy focuses on ecosystem lock-in, ensuring that iPhone users buy AirPods, MacBooks, and iPads, increasing lifetime revenue per customer.
💡 Actionable Tip: Analyze acquisition sources and double down on high-CLV marketing channels.
8️⃣ Cross-Sell & Upsell to Increase CLV
Encouraging customers to purchase complementary products boosts overall CLV.
🔹 Example:
- Amazon’s “Customers who bought this also bought” feature contributes to 35% of its total revenue.
- Subscription businesses (like meal kits and software companies) offer tiered pricing plans to encourage customers to upgrade.
💡 Actionable Tip: Introduce cross-selling (“buy together” bundles) and upselling (“premium version” upgrades) to increase customer spending per transaction.
9️⃣ Provide Seamless Checkout & Multiple Payment Options
A complicated checkout process increases cart abandonment rates, leading to lost revenue. A smooth, hassle-free checkout experience ensures higher conversions.
🔹 Example:
- Shopify stores with a one-page checkout report higher conversion rates than stores with multi-step processes.
- Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal speed up checkout, reducing friction for mobile users.
💡 Actionable Tip: Offer multiple payment options and a simplified checkout to reduce friction.
🔟 Offer Hassle-Free Returns & Customer-Friendly Policies
Making it easy to return items builds customer trust and loyalty, encouraging repeat purchases.
🔹 Example:
- Zappos’ 365-day free return policy builds customer confidence, leading to higher repeat purchase rates.
- Amazon Prime’s free returns encourage customers to shop without hesitation, increasing CLV.
💡 Actionable Tip: If revenues are exceeding expectations, consider offering free returns or extended return windows to build trust.
Final Words: Maximizing Customer Lifetime Value for Long-Term Success
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is more than just a metric — it’s a strategic approach to sustainable growth. Businesses that understand their customers’ long-term value can allocate resources effectively, optimize marketing efforts, and improve retention strategies. By focusing on high-value customer acquisition, engagement, and personalized experiences, companies can boost revenue while reducing acquisition costs.
Increasing CLV isn’t about chasing one-time transactions but about nurturing lasting relationships. The key lies in delivering exceptional customer support, leveraging personalized marketing, refining retention strategies, and using data-driven insights to continuously improve customer value. Small adjustments, like offering a seamless checkout process, expanding payment options, or implementing a loyalty program, can have a significant impact on long-term profitability.
Businesses that apply CLV-driven strategies gain a competitive edge, improve customer loyalty, and drive sustainable revenue growth. Those who neglect it risk overspending on acquisition while losing valuable repeat customers. The brands that succeed are the ones that invest in customer relationships, continuously optimize their CLV strategies, and adapt to evolving consumer behavior.
FAQ: Customer Lifetime Value Explained
What is Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)?
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is a metric that estimates the total revenue a business can expect from a customer throughout their relationship with the company. It helps businesses determine how much they should invest in acquiring and retaining customers.
Why is CLV important for businesses?
CLV helps businesses optimize their marketing spend, improve customer retention, and increase profitability. Understanding CLV allows companies to focus on acquiring high-value customers and implementing strategies that maximize long-term revenue.
How do you calculate customer lifetime value?
A basic CLV formula is:
CLV = Average Order Value × Purchase Frequency × Customer Lifespan
More advanced models consider retention rates, profit margins, and discount rates to provide a more accurate projection.
How can businesses increase CLV?
Businesses can increase CLV by improving customer retention, offering loyalty programs, personalizing marketing efforts, upselling and cross-selling, providing excellent customer support, and optimizing the checkout experience.
What is a good CLV for an e-commerce business?
The ideal CLV varies by industry, but in e-commerce, an average CLV of $150–$500 is considered strong. Subscription-based businesses typically have higher CLVs due to recurring revenue models.
What is the difference between CLV and CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost)?
CLV measures the total revenue a customer generates, while CAC represents the cost of acquiring that customer. A healthy business should have a CLV-to-CAC ratio of at least 3:1, meaning customers generate three times more revenue than it costs to acquire them.
How does customer retention impact CLV?
Retention directly influences CLV—the longer a customer stays, the higher their lifetime value. Increasing retention by just 5% can boost profits by 25-95%.
What role does personalization play in increasing CLV?
Personalized experiences improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to repeat purchases and higher CLV. Brands like Amazon, Netflix, and Starbucks use personalized recommendations and rewards to boost retention.
How often should businesses recalculate CLV?
CLV should be recalculated at least once a month to track trends, measure the impact of marketing efforts, and refine business strategies.
What tools can help businesses calculate CLV?
Businesses can use tools like Google Analytics, Optimove, WebFX CLV Calculator, and Kissmetrics to track customer behavior, segment audiences, and automate CLV calculations.