How to Get Ready for PHP 7
PHP 7 has been finally released, but are there enough reasons to migrate? Let’s take a look under its hood.

Recent benchmarks show that PHP 7 is two times faster than 5.6. You may argue that there is the HHVM platform which also shows top performance, but it is just the beginning of PHP 7, so it will become better with each new release. And what about HHVM? How long should we wait for a new generation of the project? Hence, the first reason to migrate to PHP 7 is obvious.
It is also necessary to tell a few words about deprecated features. If you are using non maintained PHP extensions, then you might have some problems with your projects. But if you don’t rely on any old stuff, you can fully leverage the new improvement. Unfortunately, it was impossible to make PHP 7 better without removing old extensions, but it was done for good.
Besides, AST now permits code optimization on the fly; fatal errors are returned in exceptions, providing the ability to treat them directly in an app; and PHP 7 includes new reserved words.
As for CMSs and frameworks, they will be updated soon, since PHP team announced all PHP 7 features in early July with the release of the beta version. Just check the below list:
- Symphony already support PHP 7;
- Zend Framework 3 will be based on PHP 7;
- WordPress also provides the ability to streamline the new technology;
- Drupal is going to provide PHP 7 support in version 8;
- Joomla will be compatible with PHP 7 after the release of 3.5;
- PrestaShop 1.1.6.2 already installs correctly with PHP 7.
As you can see, there are enough reasons to migrate to PHP 7. We strongly recommend you to rely on the official materials, while performing this complex procedure. The documentation covers all nuances of migration to PHP 7, so it is the most advanced and ultimate guide. Follow the link below to see the PHP 7 migration guide.
First of all let’s see some facts from the official PHP 7 how-to presentation. In the presentation, you can find a lot of useful comparisons of PHP 7 with PHP 5.
Table of contents
Executor
According to the available metrics it reduces the usage of CPU instructions up to 30%.
PHP 7 test suite
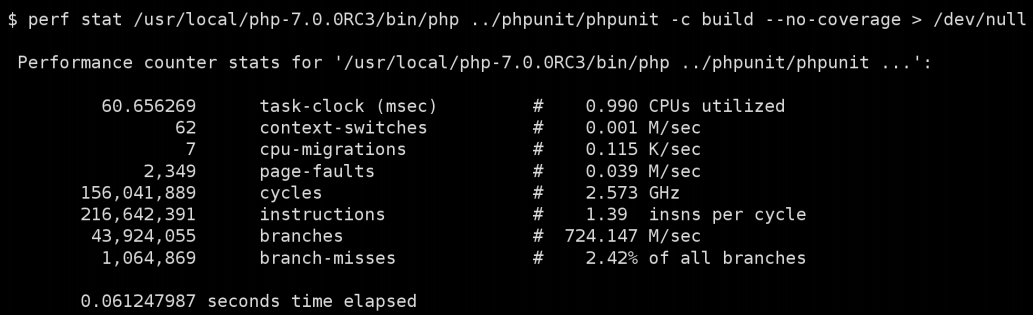
PHP 5.6 test suite
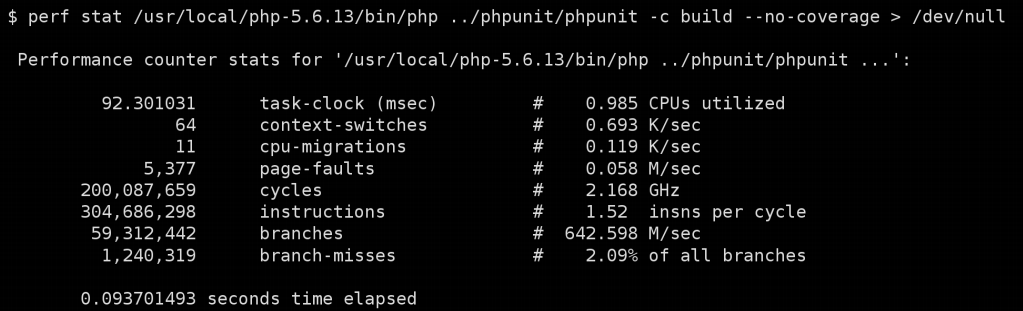
There is also a diagram showing that PHP 7 is almost 3 times faster than its predecessor:
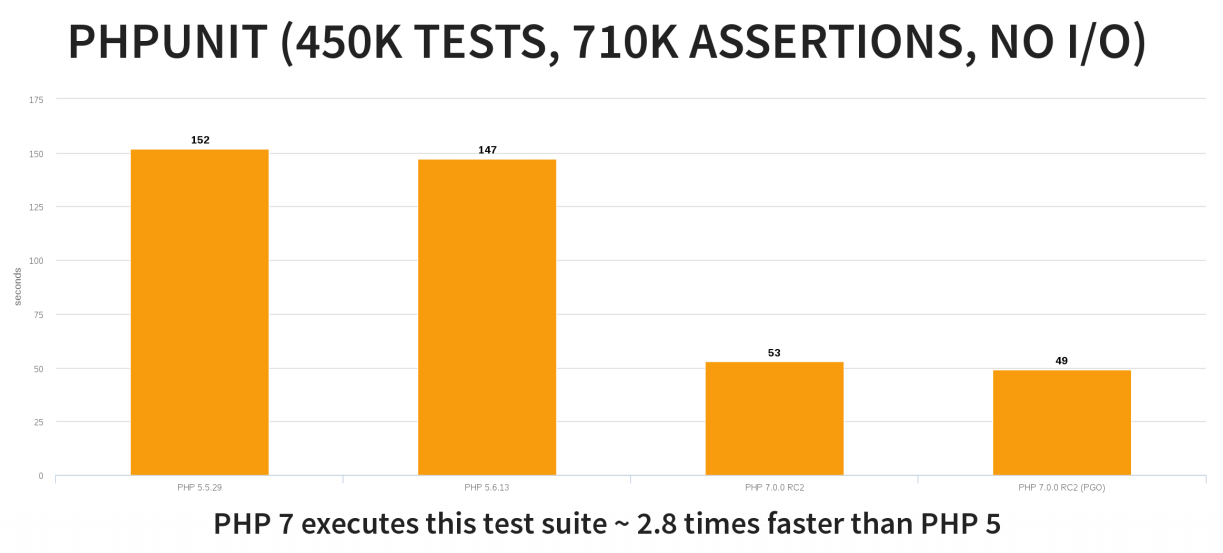
…and consumes less memory:
Compiler
Another important aspect of the update is revamped bytecode generation. Just check these screenshots:
PHP 5.6
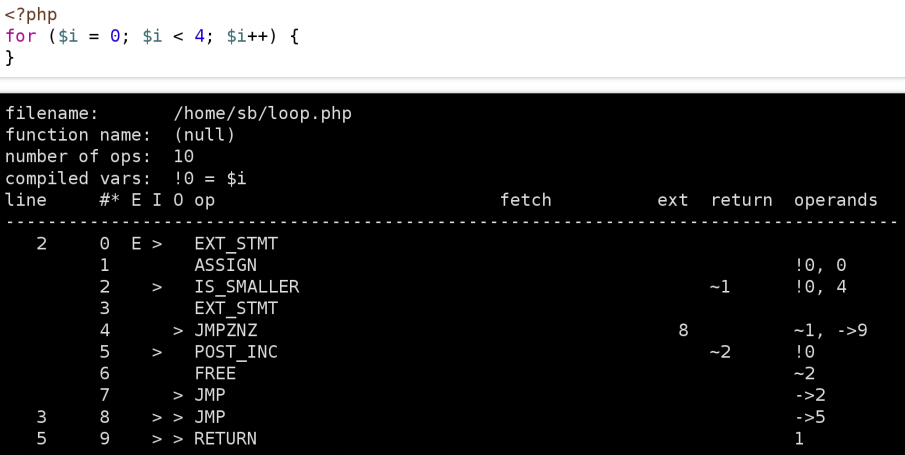
PHP 7
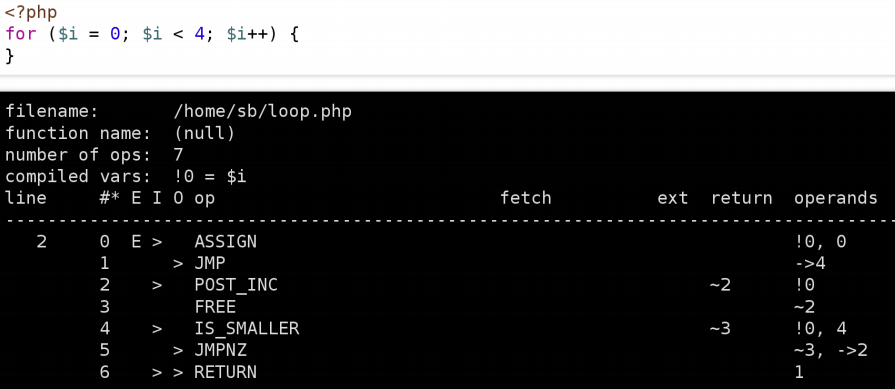
Parser
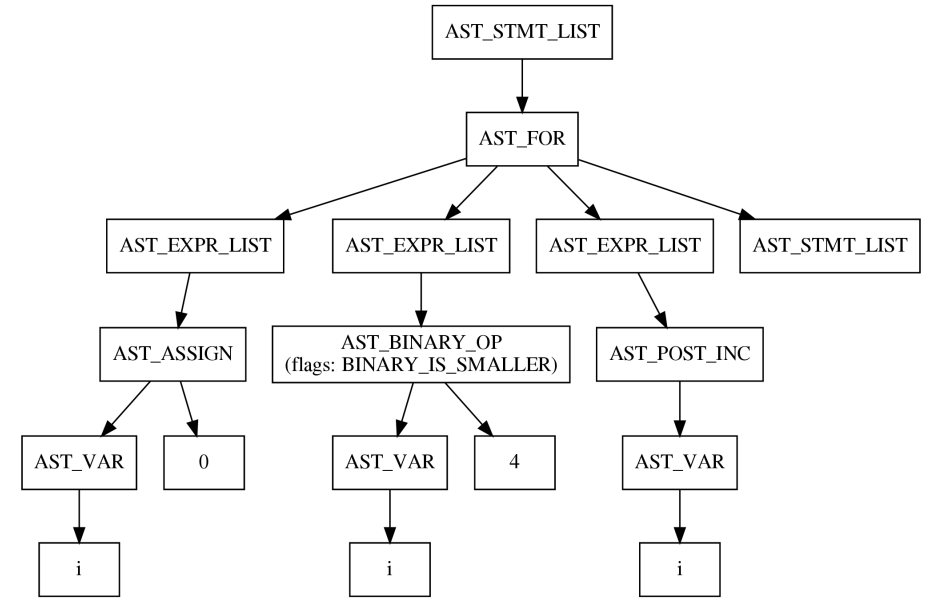
And the new version of the programming language is based on AST – Abstract Syntax Tree – with user-land access to it:
You can use the static analyzer to examine this new feature.
Lexer
Besides, PHP 7 is context-sensitive and supports semi-reserved words:
You can check the full presentation here:
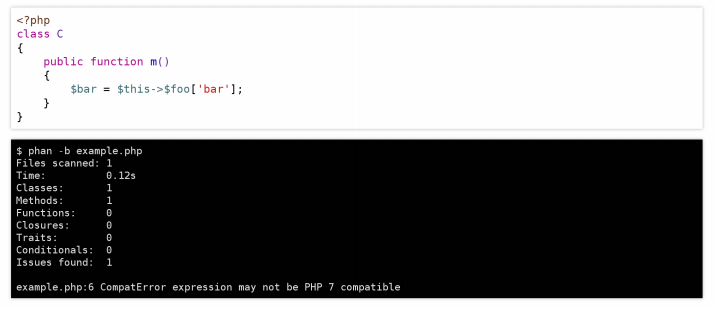
Backwards Compatibility Breaks
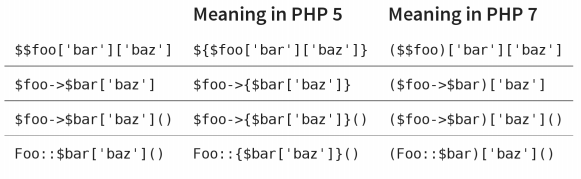
Uniform Variable Syntax is illustrated below:
New reserved Words in PHP 7 are: bool, null, object, int, false, mixed, float, true, numeric, string, resource.
As for removed deprecated features, they are represented on the following image:

Consequently, PHP 7 includes some improvements that can break your existing code, but only because of removal of deprecated functions. Thus, you should pay attention to the following new conditions:
- Both ASP and script style tags are not available in PHP 7 (<% and <script language=’php’>)
- Although ereg_ functions are removed, you can still use preg_ functions as their replacement.
- The same is about mysql_ functions, but you can use mysqli_ functions as a replacement; and about the split function – explode is its replacement.
- The usage of multiple defaults leads to a fatal error.
PHP 7 New Features
A number of new features introduced in PHP 7 will make your codding routine easier. Some major innovations are listed below:
1.
There is a new operator in PHP 7. It is called the Combined Comparison Operator or the Spaceship operator. It is designed to compare two integer values. Thus, by writing $b $c we will get 0 if both are equal, 1 in case the right side is smaller, -1 if the left side is smaller.
2.
The null coalesce operator provides the ability to set values from user input without the necessity to check if the value has been set:
|
1 2 |
$orderby = $_GET['orderby'] ?? 'date'; // equivalent to: $orderby = isset($_GET['orderby']) ? $_GET['orderby'] : 'date'; |
3.
Due to a new type hinting, PHP coders have such new scalar types as float, int, bool, and string, as well as return type hinting.
4.
As for anonymous classes, they are developed to streamline your work with unnamed classes when there is no need to document them or they are used once:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
var_dump(new class($i) { public function __construct($i) { $this->i = $i; } }); |
Now you know how to get ready for the upcoming release of PHP 7. This article contains only basic information about the new version of the language, so you should dive deep into the . We also recommend you to check other articles from the PHP 7 category on the FireBear.